Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comAs an expectant mother, you’re probably curious about every aspect of your baby’s development. One of the most crucial milestones in a baby’s journey is the development of their organs. It’s essential to understand when this process begins and what factors influence it.
Table of Contents
When Does Organ Development Begin?
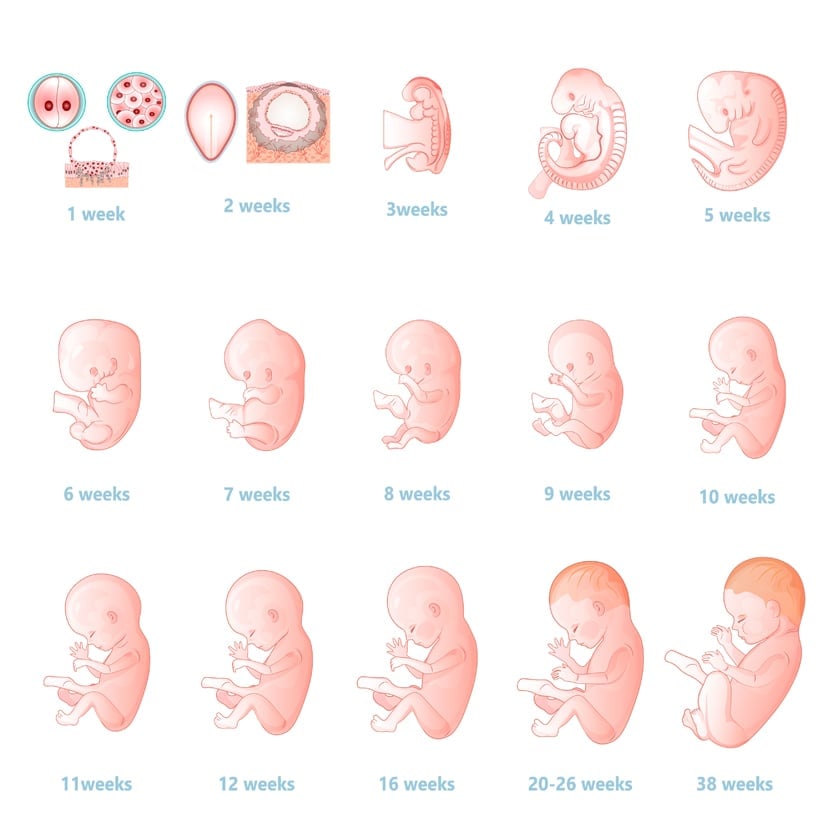
Organ development starts as early as three weeks after conception. At this point, the embryo is the size of a poppy seed, and the process of forming organs has already begun. This early stage is called gastrulation, and it’s when the cells start to differentiate, creating the basis for the baby’s organs.
During the first trimester, the development of the baby’s organs is rapid. By the end of this phase, all the major organs are present, although they are not yet fully formed or functional. The second trimester is a period of growth and maturation, and by the end of this phase, most of the baby’s organs are fully developed and functional.
Factors That Affect Organ Development
Several factors influence the development of a baby’s organs, including genetics, nutrition, and exposure to harmful substances. Genetic factors determine the baby’s susceptibility to certain health conditions and can impact the development of certain organs.
Nutrition is also critical during pregnancy, as it provides the building blocks for the baby’s organs. A lack of essential nutrients can cause developmental delays and increase the risk of birth defects. On the other hand, excessive intake of certain nutrients, such as vitamin A, can also cause harm to the developing baby.
Exposure to harmful substances, such as alcohol and tobacco, can also affect organ development. These substances can cause developmental delays, birth defects, and long-term health problems for the baby.
Commonly Asked Questions
1. Can organ development be monitored during pregnancy?
Yes, organ development can be monitored during pregnancy through various tests, including ultrasounds and amniocentesis. These tests can detect any abnormalities or developmental delays in the baby’s organs.
2. What can I do to ensure my baby’s organs develop properly?
To ensure your baby’s organs develop properly, it’s essential to maintain a healthy diet and avoid harmful substances, such as alcohol and tobacco. Regular prenatal care is also crucial, as it allows your doctor to monitor the baby’s development and detect any potential issues early.
3. Are there any warning signs of abnormal organ development?
Some warning signs of abnormal organ development include a small head size, low birth weight, jaundice, and difficulty breathing. However, some babies with organ abnormalities may not show any signs or symptoms, which is why regular prenatal care is so important.
4. Can organ development continue after birth?
Yes, some organ development continues after birth, especially in the brain and lungs. It’s important to provide your baby with proper nutrition and care to support their ongoing development after birth.
5. Can organ development be impacted by the mother’s health during pregnancy?
Yes, the mother’s health during pregnancy can have a significant impact on organ development. Poor nutrition, exposure to harmful substances, and health conditions such as diabetes can all affect the baby’s organ development.
In conclusion, organ development is a crucial milestone in a baby’s journey, and it begins as early as three weeks after conception. Several factors, including genetics, nutrition, and exposure to harmful substances, can influence this process. It’s essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle and seek regular prenatal care to ensure your baby’s organs develop properly. If you have any concerns about your baby’s development, talk to your doctor.