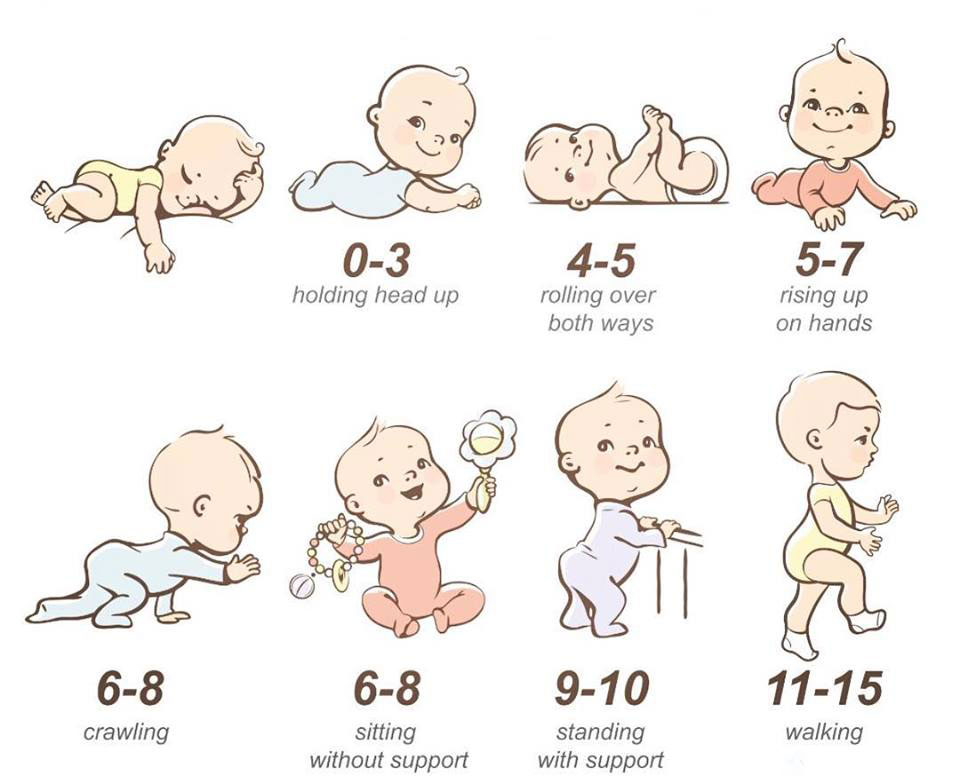
Motor development in infants is a crucial aspect of early childhood development. It refers to the development of movement skills and the ability to control muscles in the body. Infants go through several stages of motor development, starting from reflexive movements to coordinated movements that enable them to crawl, stand, and walk. Understanding motor development in infants is not only important for parents and caregivers, but also for pediatricians and other healthcare professionals.
Table of Contents
Reflexive Movements

Infants are born with several reflexes that help them survive and adapt to their environment. These reflexes include the rooting reflex, sucking reflex, and grasping reflex. The rooting reflex helps the baby find the nipple, while the sucking reflex helps them feed. The grasping reflex allows the baby to hold onto objects placed in their hand.
Gross Motor Skills

Gross motor skills are the movements that involve large muscles in the body. These skills include rolling over, crawling, sitting, standing, and walking. Infants typically start rolling over at around 4 months old, followed by crawling at around 6-8 months, and standing and walking at around 12-15 months.
Fine Motor Skills

Fine motor skills are the movements that involve small muscles in the body. These skills include grasping, holding, and manipulating objects. Infants start developing fine motor skills from birth, but it takes time for them to master these skills. By 6-8 months old, most infants can grasp and hold objects, and by 12-15 months, they can use their fingers to pick up small objects.
Sensory Development

Sensory development is closely linked to motor development in infants. Infants use their senses of sight, touch, and hearing to explore their environment and develop their motor skills. For example, a baby who has just learned to crawl will use their sense of touch to explore objects around them and their sense of sight to navigate their surroundings.
Factors Affecting Motor Development

Several factors can affect motor development in infants. These include genetics, nutrition, and the environment. For example, infants who are born prematurely may have delayed motor development compared to full-term infants. Infants who are malnourished may also have delayed motor development due to a lack of essential nutrients. The environment can also play a role in motor development, as infants who are provided with ample opportunities for movement and exploration are more likely to develop their motor skills at a faster pace than those who are not.
Early Detection of Motor Development Delays

Early detection of motor development delays is important for addressing any underlying issues that may be affecting an infant’s development. Pediatricians and other healthcare professionals use standardized assessments to monitor motor development in infants and identify any delays. If delays are detected, early intervention such as physical therapy can help improve motor development outcomes.
Conclusion
Motor development in infants is a complex process that involves several stages of development. It is important for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to understand the different stages and factors that can affect motor development. Early detection of motor development delays is crucial for addressing any underlying issues and ensuring that infants achieve their full motor development potential.
Related Articles:
- 10 Tips for Encouraging Motor Development in Infants
- How to Identify Motor Development Delays in Infants
- The Role of Nutrition in Motor Development
- The Importance of Tummy Time for Infants
- Physical Therapy for Infants with Motor Development Delays
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are gross motor skills?
Gross motor skills are the movements that involve large muscles in the body, such as rolling over, crawling, standing, and walking.
What are fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills are the movements that involve small muscles in the body, such as grasping, holding, and manipulating objects.
What factors can affect motor development in infants?
Factors that can affect motor development in infants include genetics, nutrition, and the environment.
How can I encourage motor development in my infant?
You can encourage motor development in your infant by providing ample opportunities for movement and exploration, providing age-appropriate toys and activities, and engaging in tummy time.
What should I do if I suspect my infant has a motor development delay?
If you suspect your infant has a motor development delay, talk to your pediatrician or healthcare provider. Early intervention such as physical therapy can help address any underlying issues and improve motor development outcomes.